A format pattern is a string and can be used for specifying patterns to format strings, which are in XML instance. JReport format patterns only supports specifying patterns to format time data type strings, such as date, time and datetime. You can customize the format pattern for date, time and datetime formats or use default ones.
In the process of transforming an XML schema to relational tables, you can choose to customize the format patterns for date, time and datetime formats in the XML schema or apply the default ones, which will comply with the W3C XML Schema 1.1 specification (for details, refer to the page http://www.w3.org/TR/2004/REC-xmlschema-2-20041028/datatypes.html#dateTime). See the following contents of the section to know more about the customized format patterns.
You can specify the date, time and datetime formats in XML schema by the date, time and datetime pattern strings or customize the format pattern by the Format Pattern dialog. In the dialog, the pattern string you select from the Pattern String list box will be interpreted, and the delimiter that you input will not be interpreted. Any character is acceptable and it will be quoted if necessary.
Within date, time and datetime pattern strings in the XML schema, unquoted letters from A to Z and from a to z are interpreted as pattern letters representing the components of a date, time or datetime string. Text can be quoted using single quotes (') to avoid interpretation. '' represents a single quote. All other characters are not interpreted; they're simply copied into the output string during formatting or matched against the input string during parsing the XML schema.
A format pattern consists of some pattern strings and delimiters. The following pattern strings that JReport Designer provides you to use in the format pattern: G, yyyy, yy, MMMM, MM, dd, D, WW, ww, F, E, a, HH, kk, KK, hh, mm, ss, SSS, z, Z.
The following table describes the detail information of the pattern strings listed above:
| Letter | Date Component | Presentation | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| G | Era designator | Text | AD |
| y | Year | Year | 1996; 96 |
| M | Month in year | Month | July; Jul; 07 |
| w | Week in year | Number | 27 |
| D | Day in year | Number | 189 |
| d | Day in month | Number | 10 |
| F | Day of week in month | Number | 2 |
| E | Day in Week | Text | Tuesday; Tue |
| a | Am/pm marker | Text | PM |
| H | Hour in day (0-23) | Number | 0 |
| k | Hour in day (1-24) | Number | 24 |
| K | Hour in am/pm (0-11) | Number | 0 |
| h | Hour in am/pm (1-12) | Number | 12 |
| m | Minute in hour | Number | 30 |
| s | Second in minute | Number | 55 |
| S | Millisecond | Number | 978 |
| z | Time zone | General time zone | Pacific Standard Time; PST; GMT-08:00 |
| Z | Time zone | RFC 822 time zone | -0800 |
When the year string of a datetime data in the XML schema is parsing, only strings consisting of exactly two digits will be parsed into the default century. Any other numeric string, such as a one-digit string, a three or more digit string, or a two-digit string but one is a sign (for example, -2), is interpreted literally. So 03/06/4 or 03/06/004 is parsed, using the pattern of MM/dd/yy, as Mar 6, 4 AD. Also, 03/06/-4 is parsed as Mar 6, 5 BC.
|
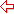
Hours must be between 0 and 23, and Minutes must be between 00 and 59.
|
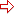
TwoDigitHours must be between 00 and 23.
Format pattern also supports localized date, time and datetime pattern strings. In these strings, the text presentation of pattern letters described in the above table may be varied with the locale.
The representation of the format pattern for date data type in XML schema is same as datetime but the pattern strings are less than it. Only the following strings can be used: G, yyyy, yy, MMMM, MM, dd, D, WW, ww, F, E.
The representation of the format pattern for time data type in XML schema is same as datetime but the pattern strings are less than it. Only the following strings can be used: a, HH, kk, KK, hh, mm, ss, SSS, z, Z.