Merging catalogs
Two catalogs can be merged. The merge operation occurs when you save a report to another directory in which a catalog of the same name already exists.
Specifying the checking level
When merging catalogs, JReport Designer will check for differences between the two catalogs. You can specify the checking level to suit your requirements.
To specify the checking level:
- Click File > Options. The Options dialog displays.
- In the Catalog category, select the required level in the Merge Catalog box. Options are:
- Identify All Differences
JReport Designer will check for all differences between the two catalogs. All the resources of the report will be displayed in the Merge dialog with all the conflicting resources marked.
- Identify Critical Differences
JReport Designer will check for differences that can cause the engine to fail when running the report. All the resources of the report will be displayed in the Merge dialog with any critical conflicting resources marked. As a result, when this option is selected, some different values may be returned when you run the saved report later.
- Ignore Differences
Does not show differences between the two catalogs. If there are conflicts, they will remain in the resources of the target catalog. As a result, when this option is selected, a saved report might not run later.
- Click OK in the Options dialog to accept the settings.
When you merge the two catalogs, resources that have the same mapping names in the two catalogs may conflict with each other (have different property values). JReport Designer will check the differences for you according to the level specified.
Merging catalogs
With the checking level specified, you can then start to merge catalogs.
- Open a report in the catalog that you want to merge with another catalog.
- Click File > Save To on the menu bar. The Save To dialog appears.
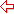
- Choose a directory where a catalog of the same name exists, and then save the report. If you specified the checking level as Identify All Differences or Identify Critical Differences, the Merge dialog will be displayed for dealing with conflicting resources. See the dialog.
- Highlight one conflicting resource in the resources to be merged box, and then select the operations:
- Rename - Renames the selected conflicting resource, and copies it to the target catalog with a new name.
- Replace - Replaces the target catalog with the selected conflicting resource from the source catalog. In this case, the reports that use this object in the target catalog will be impacted.
- Skip - Keeps the value in the target catalog for the selected conflicting resource. In this case, the report that uses this object in the source catalog will be impacted.
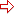
- Click the Differences button and the Properties Differences dialog appears. See the dialog.
The properties values of the conflicting resource from the two catalogs will be displayed in this dialog with any differences highlighted. Click the Previous / Next button in the dialog, and it will go to the previous/next conflicting resource. Click Close to close the dialog.
- Click the Target Relation button in the Merge dialog.
The name of the resource and its parent node in the target catalog will then be displayed in the Target Relation dialog.
For example, sometimes a resource is marked in the Merge dialog, but in the Properties Differences dialog, no difference is shown between the two resources. In this case you can use this button to check whether the parent nodes of the two resources are different.
- Click Close to close the Target Relation dialog box and return to the Merge dialog.
- Click the Merge button when you finish. JReport Designer will save the report according to the changes that you have made.
- Publish the catalog and the reports and test to ensure all the reports are working properly.
Notes:
- Sometimes, though some objects are marked in the Merge dialog, in the Properties Differences dialog, you will not find these differences. The reason is that some children of the two objects are different.
- JReport Designer checks parameters based on the whole catalog. For example, assume that there is a parameter named Param1 in DataSource1 of the source catalog, and there is also a parameter named Param1 in DataSource2 in the target catalog. These two parameters in different connections will be checked as a conflicting resource. You must rename the parameter in order to get a correct result.



